Introduction
In the era of rapid digitization, organizations are increasing Artificial Intelligence (AI) to optimize their workflows, aiming to boost work efficiency and overall productivity. Recent years have witnessed the ascension of AI as a revolutionary technology that can help create content, analyze data, and perform tasks with the highest accuracy which is unattainable with human resources. At the forefront of this technological evolution is Generative AI with its own limitations, and advantages it is a system connecting neural networks to separate intricate patterns and structures within the existing data, subsequently generating novel and authentic data. Notably, applications such as Chatbots and Virtual assistants have been successfully employed in creating advanced technology that can understand and respond to the natural language.
As these intelligent systems continue to advance in sophistication, a pivotal question arises: Will they serve to augment the capabilities of professionals, becoming invaluable collaborators or does the path of AI development pose a potential threat to human expertise? The exploration explores the transformative potential of Generative AI, navigating the fine line between augmentation and substitution in the professional landscape.
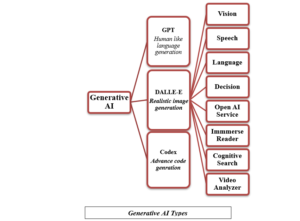
Generative AI and Human Intelligence
Generative artificial intelligence stands as a captivating frontier that has captivated the attention across professional and personal spheres alike. Generative AI has the potential to cause a change in many aspects of life, more specifically it utilizes machine learning, neural networks, and other techniques to generate new content (text, images, and music) by analyzing patterns and information from the training data. The essence of generative AI lies in its capacity to sift through extensive datasets, discern patterns, and craft outputs that can be valuable to human creations. This capability has made generative AI indispensable across various industries, serving as a powerful tool for innovation and efficiency. Yet, it is crucial to recognize that the relationship between humans and AI is not one of isolation rather it represents a parallel journey. Human intelligence assumes a pivotal role in complementing AI, synergising the strength to unlock the greater gates in productivity. In this symbiotic relationship, human originality remain irreplaceable that harmonizes seamlessly with the capabilities of generative AI.
Complementary Aspects of Generative AI
- Collaborative Creativity: AI can generate new and unique ideas based on the existing data but sometimes AI can lack the creativity and imagination that a human possesses. Human professionals can provide innovative ideas that can be further refined with the help of generative AI.
- Personalized Customer Experience: In various industries like retail and marketing, the demand by people for personalized experiences is paramount. Generative AI plays a crucial role in analyzing customer preferences and behaviors. By doing this, it enables the creation of highly personalized recommendations tailored to individual needs. For example, In marketing, generative AI can efficiently generate personalized content and automate ad campaigns. This not only enhances the customer engagement but it also empowers marketers to focus on developing strategic campaigns that align with the specific preferences of their target audience
- Language Translation and Communication: AI-powered tools play a pivotal role in facilitating seamless communication for professionals navigating diverse linguistic landscapes. These tools serve as an invaluable asset in international business and diplomacy by breaking down language barriers. Through advanced translation capabilities, AI empowers professionals to engage in effective cross-cultural exchanges. Furthermore, AI aids in efficiently summarizing substantial volumes of written data, enabling professionals to glean essential information easily.
- Learning and Skill development: Generative AI emerges as a transformative force in learning and skill development, mainly in the realm of surgical training. By crafting realistic scenarios within virtual environments, AI replicates the intricate details of actual operating rooms where the surgeons can immerse themselves in the stimulated environments such as lighting conditions, equipment intricacies, and the anatomy of the patients. This provides a controlled and safe environment to refine their expertise.
- Data management: In a matter of seconds AI systems possess the capability to efficiently process vast volumes of data, unveiling valuable insights that hold substantial potential for human professionals. This rapid and meticulous data processing not only expedites the analytics process but also equips professionals with a wealth of information essential for making well-informed decisions.
Job Transformation
While generative AI has the potential to complement human professionals, it also brings a transformation in job roles. The advent of generative AI introduces a paradigm where routine and repetitive tasks traditionally performed by humans, are automated with exceptional efficiency.
This transformative wave in the workforce landscapes underscores the need for human professionals to cultivate new skills and competencies among themselves with the changing times. The evolution in the job roles necessitates a proactive and strategic approach to education and training, professionals must engage in continuous learning initiatives to stay abreast of the latest advancements.
Every organization must understand the limitations of AI:
- Emotional Intelligence and empathy: In every organization, there must be empathy among the employees to foster trust, and promote open communication and support to the employees in resolving the conflicts or providing personalized support to the employees. AI in this situation can not relate to human emotions, while it can somewhat gauge emotional states, it cannot replicate genuine empathy.
- Complex decision-making and ethical Consideration: Human professionals often face complex situations in the organization that demand strategic decision-making and ethical considerations. AI even though highly advanced cannot understand its decisions at a broader context. For example: if historically, the company has hired more candidates from a specific gender, ethnicity, or university, the AI algorithm may learn and perpetuate these biases.
- Career Development and Mentorship: Career development and mentorship are integral to promoting growth, AI cannot build the meaningful relationships necessary for effective mentorship. Human professionals can act as mentors, offering personalized guidance, support, and encouragement contributing significantly to the employees’ job satisfaction.
Conclusion
The trajectory of generative AI points towards a future defined by a collaboration between human ingenuity and machine intelligence. Rather than usurping human roles generative AI is more likely to become a collaborative partner, amplifying human capabilities and empowering professionals to engage in more sophisticated tasks that demand human expertise. The key lies in embracing the collaborative potential of generative AI while proactively addressing ethical considerations and preparing the workforce for the inevitable transformations that lie ahead.
In this collaborative landscape, AI emerges not as a substitute but more as a complement that will act as a valuable tool that when integrated thoughtfully will enhance productivity and also unlock novel possibilities. By cultivating a symbiotic relationship between humans and AI we pave the way for the future where innovation, creativity, and productivity flourish in tandem, creating a workplace that maximizes the potential of both human and machine intelligence. A balanced approach that combines the strengths of AI with an empathetic understanding of human intelligence will lead to more effective practices and a more harmonious work environment.
